What is Footprinting?
by : Vyshu <vaishnavu c v >
Footprinting is basically the first step where hacker gathers as much information as possible to find ways to intrude into a target system or at least decide what type of attacks will be more suitable for the target.
Footprinting is a part of the reconnaissance process which is used for gathering possible information about a target computer system or network. Footprinting could be both passive and active. Reviewing a company’s website is an example of passive footprinting, whereas attempting to gain access to sensitive information through social engineering is an example of active information gathering.
During this phase, an ethical hacker can collect the following information
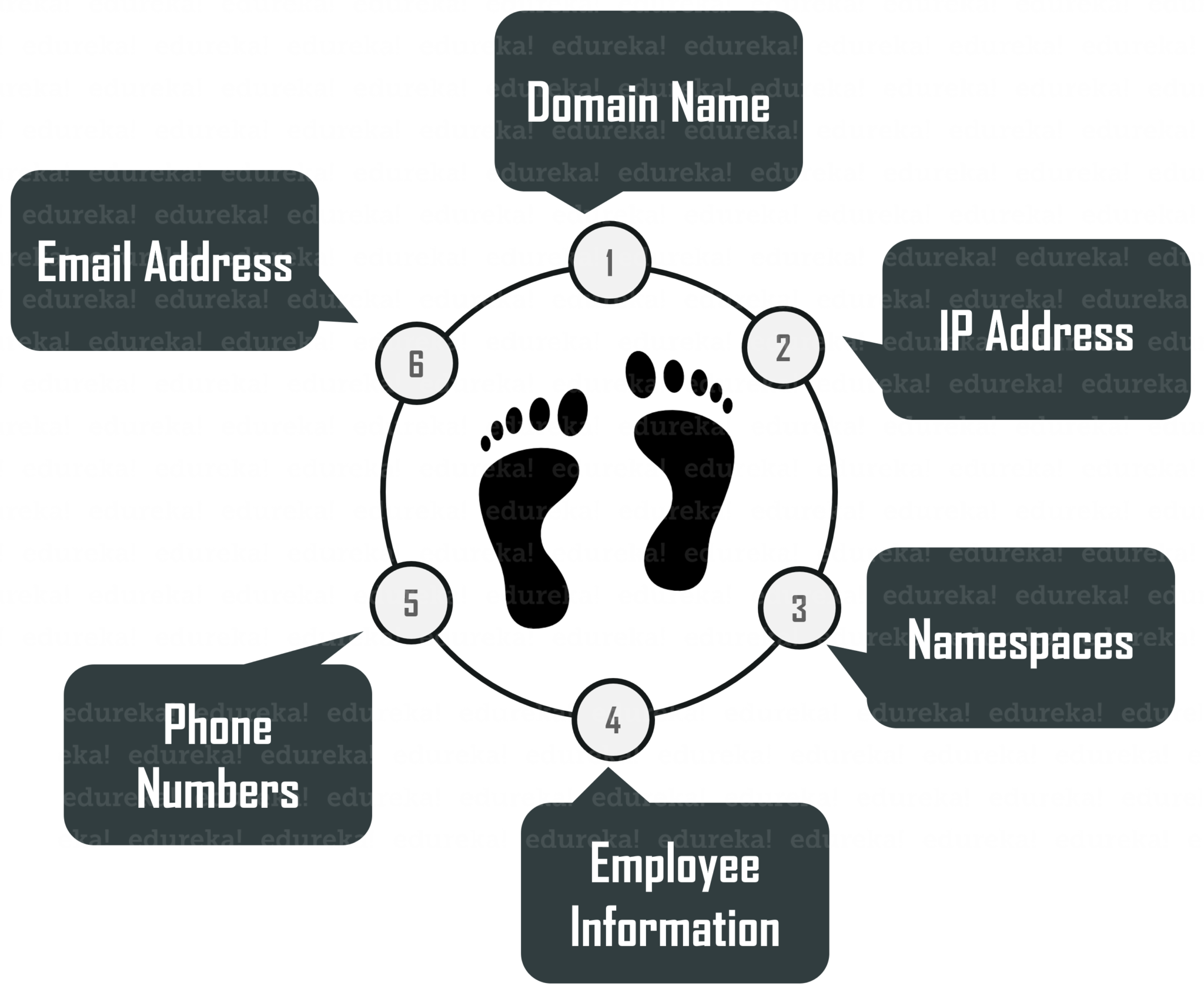
Footprinting – What is ethical hacking – Edureka
General footprinting is really simple and even an everyday user could do it using websites like whois.com, ip2location.com, archive.org etc
What is Fingerprinting?
Fingerprinting, in ethical hacking, refers to any method that is used to determine the operating system that is being run on the target computer. Fingerprinting, much like Footprinting is both active and passive
Active Fingerprinting
Active fingerprinting is accomplished by sending specially crafted packets to a target machine and then noting down its response and analyzing the gathered information to determine the target OS. In the following section, we have given an example to explain how you can use NMAP tool to detect the OS of a target domain.
Passive Fingerprinting
Passive fingerprinting is based on sniffer traces from the remote system. Based on the sniffer traces (such as Wireshark) of the packets, you can determine the operating system of the remote host. Before attacking a system, it is required that you know what operating system is hosting a website. Once a target OS is known, then it becomes easy to determine which vulnerabilities might be present to exploit the target system. Fingerprinting is done by analyzing various factors of a packet
- TTL − What the operating system sets the Time-To-Live on the outbound packet.
- Window Size − What the operating system sets the Window Size at.
- DF − Does the operating system set the Don’t Fragment bit.
- TOS − Does the operating system set the Type of Service, and if so, at what.
By analyzing these factors of a packet, you may be able to determine the remote operating system. This method is not 100% accurate and works better for some operating systems than others.
Footprinting helps to
Know Security Posture – The data gathered will help us to get an overview of the security posture of the company such as details about the presence of a firewall, security configurations of applications etc.
Reduce Attack Area – Can identify a specific range of systems and concentrate on particular targets only. This will greatly reduce the number of systems we are focussing on.
Identify vulnerabilities – we can build an information database containing the vulnerabilities, threats, loopholes available in the system of the target organization.
Draw Network map – helps to draw a network map of the networks in the target organization covering topology, trusted routers, presence of server and other information.
Footprinting Methodology
Various methods used to collect information about the target organization. They are
Footprinting through Search Engines
This is a passive information gathering process where we gather information about the target from social media, search engines, various websites etc. Information gathered includes name, personal details, geographical location detrails, login pages, intranet portals etc. Even some target specific information like Operating system details, IP details, Netblock information, technologies behind web application etc can be gathered by searching through search engines
Eg: collecting information from Google, Bingo etc

Google Hacking:
Google hacking refers to collecting information using google dorks (keywords) by constructing search queries which result in finding sensitive information.details collected include compromised passwords, default credentials, competitor information, information related to a particular topic etc.
Eg:inurl:, site:, allintitle etc
Examining HTML Source and Examining Cookies:
Html source codes of a web application may give us an understanding of the application functionality, hidden fields, comments, variable names etc. Cookies are used to identify a user in his session. these cookies may be stored in the browser or passed in the URL, or in the HTTP header.
The entire website can be mirrored using tools like HTTtracker to gather information at our own phase.
Extract website Archives: older versions of website can be obtained
which may reveal some information related to the target.
eg: www.archive.org
Email Footprinting
email header reveals information about the mail server, original sender’s email id, internal IP addressing scheme, as well as the possible architecture of the target network
Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence gathering is the process of gathering information about the competitors from resources such as the Internet.
Eg: company website, search engine, internet, online databases, press releases, annual reports, trade journals
Google Hacking/Google Dorks
This is a process of creating search queries to extract hidden information by using Google operators to search specific strings of text inside the search results.
Some google operators, site, allinurl, inurl, allintitle
Whois Footprinting
Whois databases and the servers are operated by RIR - Regional Internet Registries. These databases contain the personal information of Domain Owners. Whois is a Query response protocol used for querying Whois databases and its protocol is documented in RFC 3912. Whois utility interrogates the Internet domain name administration system and returns the domain ownership, address, location, phone numbers, and other details about a specified domain name.
DNS Footprinting
DNS is a naming system for computers that converts human-readable domain names into computer readable IP-addresses and vice versa.DNS uses UDP port 53 to serve its requests. A zone subsequently stores all information, or resource records, associated with a particular domain into a zone file; Resource records responded by the name servers should have the following fields:
-
Domain Name — Identifying the domain name or owner of the records
-
Record Types — Specifying the type of data in the resource record
-
Record Class — Identifying a class of network or protocol family in use
-
Time to Live (TTL) — Specifying the amount of time a record can be stored in cache before discarded.
-
Record Data — Providing the type and class dependent data to describe the resources.
A (address)—Maps a hostname to an IP address
SOA (Start of Authority)—Identifies the DNS server responsible for the domain information
CNAME (canonical name)—Provides additional names or aliases for the address record
MX (mail exchange)—Identifies the mail server for the domain
SRV (service)—Identifies services such as directory services
PTR (pointer)—Maps IP addresses to hostnames
NS (name server)—Identifies other name servers for the domain
HINFO = Host Information Records
DNS servers perform zone transfers to keep themselves up to date with the latest information. A zone transfer of a target domain gives a list of all public hosts, their respective IP addresses, and the record type.
Footprinting through Social Engineering:
Social media like twitter, facebook are searched to collect information like personal details, user credentials, other sensitive information using various social engineering techniques. Some of the techniques include
- Eavesdropping: It is the process of intercepting unauthorized communication to gather information
- Shoulder surfing: Secretly observing the target to gather sensitive information like passwords, personal identification information, account information etc
- Dumpster Diving: This is a process of collecting sensitive information by looking into the trash bin. Many of the documents are not shredded before disposing them into the trash bin . Retrieving these documents from trash bin may reveal sensitive information regarding contact information, financial information, tender information etc.
- Footprinting countermeasures:
- Creating awareness among the employees and users about the dangers of social engineering
- Limiting the sensitive information
- encrypting sensitive information
- using privacy services on whois lookup database
- Disable directory listings in the web servers
- Enforcing security policies
For more information regarding cybersecurity, you could check out my other blogs..
Comments
Post a Comment